Laser Scanning
Laser scanning technology is particularly beneficial in brownfield projects, where existing infrastructure, operational complexities, and safety concerns pose unique challenges.
Laser scanning enables you to easily determine the changes carried out on site that are not reflected in any drawing and the difference between actual, most probably deviated items of the plant and drawings issued for construction long ago and/or based on the aging of the plant and/or built, fabricated and/or installed not as per drawings which might mislead you.
Here are specific benefits, considerations, and drawbacks of utilizing laser scanning brownfield projects.
Precise As-Built Documentation
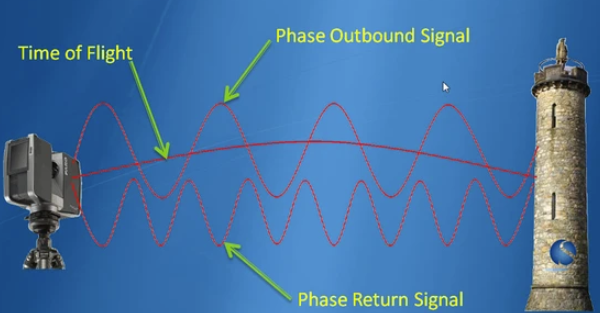
Laser scanning technology provides high-definition 3D data, capturing all details of the plant, including pipes, electrical & instrumentation, equipment, and structures within millimeter accuracy.
This precision is crucial to assess the coordinates of equipment, especially coordinates of their nozzles and foundations, pipes, structures, and existing conditions, especially in complex industrial settings.
It captures not only the geometry but also surface details, textures, and spatial relationships between different elements. This comprehensive data set allows for a thorough understanding of the site’s current state.
Precise as-built documentation, which can be obtained based on laser scanning data, accommodates as a baseline for future projects, assisting to understand the current state of the infrastructure and plan accordingly.
Please consider that storing high-definition data will consume a large amount of data storage and increase data storage costs.
Efficiency in Data Acquisition and Time Savings
In comparison to site surveys and dimensions taken manually on-site, laser scanners can capture millions of data points per second, allowing large areas to be scanned in a relatively short period with millimetric accuracy. This efficacity reduces manhours spent on-site, which is advantageous in active and/or hazardous environments.
The non-intrusive nature of laser scanning means that data can be collected without interrupting ongoing operations. This is crucial in brownfield sites where business continuity and safety are priorities.
Please consider that access restrictions to certain areas of the plant due to leakage, corrosion, and other safety concerns may lead to not covering all areas by scanning, and harsh weather conditions such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, and dusty environment may lead to downtime of executing of laser scanning site activities.
Some of the equipment and software work very efficiently together, but in other cases, similar manhour schedules for ‘post-processing’ activities should be considered in advance, in comparison to laser scanning activities on-site related to combining targets to obtain point cloud network and noise effects cleaning.
Noise effects are the effects caused by ambient temperature, humidity, reflective surfaces, rain, snow, heavy gusts, dust, vapors, and gases. The cleaning process of noise effects is highly important in order to receive precise data in case of hiring contractors to carry out laser scanning activities. Thus, mechanisms of control of received data are of utmost importance and should be utilized parallel to post-processing activities before data submission.
A Guide Book on Pipe Drafting and Design
Assessment of the shadow areas (term used for areas not covered areas because of other objects such as column, drum, or pipe rack elevations in the way of a laser beam or other issues caused) during the site execution and after during the post-processing step should be carried out prior to data delivery. If a company hires contractors for laser scanning execution, assessment should be carried out by the client and/or another contractor or engineering company that will carry out 3D modeling based on the laser cloud input. An execution plan should be agreed upon to cover shadow areas as much as possible to leave the least areas not covered by laser scan, based on this assessment.
Nowadays, it is not as hard as it was to cover shadow areas by considering the variety of equipment (such as hand scanners, drones, airborne, etc., in addition to conventional laser scanners with tripods) that can be combined to obtain laser clouds with less and less shadow areas.
Improved Planning, Design, and Analysis
The data collected can be used to create precise 3D models, which are invaluable for design purposes. These models help visualize the project and make informed decisions during the design phase.
By integrating the scanned data into CAD or BIM software, potential clashes between new designs and existing structures can be detected early. This proactive approach prevents costly modifications and delays during construction.
Detailed 3D models allow for precise measurement and quantity takeoff, aiding in the precise estimation of materials and costs. This ensures that budgeting is more precise and resources are optimally allocated.
Detailed models help identify potential clashes or interference between new and existing structures, which is crucial for planning maintenance activities or retrofitting new equipment.
Optimization for shutdown planning can be executed with the assistance of precise maintenance data, ensuring that all necessary work can be completed efficiently and safely within the scheduled downtime.
Safety Improvements
Laser scanning can often be conducted from a safe distance, reducing the need for personnel to enter potentially hazardous areas. This minimizes the risk of accidents and enhances overall safety on the site.
Detailed documentation of the existing conditions helps in planning safe demolition or revamp activities.
Laser scan data may assist in executing safety inspections and risk assessments by identifying potential leaks, corrosion, and structural weakness-caused hazards from the office environment, which will flourish in safety measures.
Cost Effectiveness and Mitigation of Risks
The speed and accuracy of laser scanning reduce the need for prolonged site visits and manual measurements, minimizing downtime and disruption to ongoing operations.
Precise data reduces the likelihood of errors in the design and construction phases, minimizing the need for rework. This translates into significant cost savings and helps in staying within budget by reducing time consumption of rework and change orders.
Precise data aids in better resource allocation, reducing waste, and optimizing material use, which can significantly cut costs. This leads to optimized project timelines and cost management.
The initial cost of purchasing laser scanning equipment, required software, investing in personnel training, and/or hiring experienced personnel could be high and should be considered for operating companies. Therefore, hiring contractors will be more effective than building teams for operating companies.
On the other hand, investing in laser scanning equipment, software, and human resources will be very beneficial for brownfield engineering and design companies in the short and long term.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
3D models and visual images obtained from laser scan data can be used to effectively establish communication plans and progress with stakeholders, including clients, contractors, and regulatory authorities. This transparency assists in establishing trust and alleviates collaboration.
Precise data and visual models improve coordination among different teams involved in the project. Engineers, architects, and contractors can all work from the same precise base data, reducing misunderstandings and ensuring that all parties are aligned.
Laser scanning provides comprehensive documentation, which is invaluable for compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes environmental assessments, safety inspections, and ensuring adherence to industry standards.
Detailed as-built models can be used to support permitting processes, providing regulators with a clear view of the facility’s current state and any planned modifications.
· Data Integration and Advanced Analysis
The data obtained from laser scanning can be seamlessly integrated into BIM and CAD systems, enhancing the accuracy and detail of project documentation. This integration is vital for modern construction practices, where Digital Twins and BIM are increasingly becoming the new standard of the industry.
Precious datasets can be used for various advanced analyses, such as structural integrity assessments, thermal performance studies, and analyses of environmental impacts. These analyses provide crucial perceptions that enlighten design and construction determination, guaranteeing compliance with sustainability and regulation targets.
The precise data from laser scans can be used to monitor the condition of assets over time, identifying wear and tear, corrosion, or structural issues before they become critical.
The detailed documentation supports lifecycle analysis, helping in making informed decisions about repairs, upgrades, or decommissioning of assets.
In summary, laser scanning offers an inclusive, productive, and safe method for seizing detailed intelligence about brownfield sites. This technology enhances planning, design, safety, cost efficiency, and collaboration, making it an invaluable tool for brownfield projects.