Pipe Spool Installation In Pipe Rack
In this blog, we will delve into the process of installing pipe spools in pipe racks. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the field, this guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of the entire installation process. This blog can also be used as a method statement for any project’s piping installation team.
We will cover every crucial aspect, including:
Number of Personnel: Learn about the team composition and the specific roles required for a successful installation.
Duties of Personnel: Descriptions of the responsibilities and tasks assigned to each team member.
Required Tools and Equipment: A comprehensive list of all the necessary tools and equipment to ensure an efficient and safe installation process.
Method of Installation: This section provides step-by-step instructions on the installation procedure, including best practices and tips for achieving optimal results.
Consumables
Health, Safety, and Environmental (HSE) Requirements: Essential safety protocols and environmental considerations to ensure a safe working environment.
Quality Requirements: Standards and checkpoints to maintain the highest quality throughout the installation process.
Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to perform pipe spool installations effectively and safely.
PERSONNEL
A standard pipe erection team consists of a leader, one or two pipe fitters, two helpers, and a welder. The number of piping crew members may change depending on the pipe length or size. Related foremen control these teams. Whenever required, the scaffolding team joins the support erection team. The lifting and transportation team comprises crane operators, riggers, drivers, etc. They serve and join the erections group when lifting and transporting straight pipes and pipe spools to the site.
In addition to the groups above, planning, survey, QA/QC, and HSE teams shall be established to serve the groups mentioned above.
EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS
All portable electrical equipment must pass the PAT test and be labeled with the next test indication date. No equipment should be used with an outdated PAT test. The capacity of the tools may change, depending on the size and weight of the pipe spools.
Welding Machines and Tools (Torches, cables, pens, etc.)
Various hand tools and wrench sets
Tirfor Capacity: various capacities
Chain Block Capacity: various capacities
Grinder
Pipe Roller Capacity: 3 tonnes – 5 tonnes and 10 tonnes
Beam Clamp Capacity: 5 and 10 tonnes
Hydraulic jack Capacity: 100 tonnes
Pipe stands Capacity: 5 tonnes and 10 tonnes
Pipe clamp 10” to 36”
Threading Machine
Pipe Wrench
CONSUMABLES
Cutting disks (CS and SS), Size 115&180
Grinder disks (CS and SS), Size 115&180
Rope for alignment
Marker pen in different colors (Company approved)
Tapes for weld joint wrapping (Company Approved)
Cleaning cloths
Electrodes
Shim plates
Pipe bars, cone-shaped support
Signboards
Welding Tents
Flapper Wheels
Threading Sealant
End Caps / Foam (purge) dams, water soluble paper
METHOD STATEMENT
CLEANLINESS
1- The end cover will be removed just before the fit-up and pipe rack assembly of the new piping. The Pipe Foreman or Pipe Fitter will verify the internal cleanliness prior to fit-up. Pre-set welds shall be checked for cleanliness as well. The fit-up joint tape shall be removed and checked for cleanliness before pre-heat and welding activities.
2- All spools shall be blown through by an air compressor just before the erection, and the spool cleanliness report shall be filled. Internal pipe mechanical cleaning and air-blown cleaning may be required for large-bore piping. Hand brushes, air lances, and cloth rags shall be used for cleaning activities. These works require a confined space entry permit, and related precautions like a gas test, stand-by man, and any others shall be discussed with the HSE department.
3- Below activities shall be performed by Craftsman and/or Foreman;
· Remove Protection.
· Inspect open end for internal cleanliness
· Clean (blowing with compressed air), QC should verify internal cleanliness and prepare related forms if necessary.
· Initial and date on pipe with the approved paint marker.
· After erection, installation, and welding, return undamaged pipe covers to a storage area for future use.
4- The field pipe crews are responsible for initialling the pipe connection using a chloride free paint marker (approved by Company) to verify the inspection.
5- Under no circumstances any item (including welding consumable) shall be temporarily stored inside the pipes.
6- The field pipe crews are responsible for covering all open ends at all times when work is not in progress (during lunch breaks, overnight, end-of-shift periods, or weekend periods).
7- Where butt welds are left in “tack welded” condition, chloride-free tape shall be wrapped around the joint to prevent any ingress of dust and water due to the weather conditions.
8- All flange gasket surfaces shall be protected by 10mm thick plywood or plastic flange covers secured by wires; in addition, lubricating grease shall be applied to all flange faces. When plywood covers are used, a polyethylene sheet shall be placed between the coated flange face and cover to prevent cover from absorbing the grease.
PREPARATION
1- Before erection works start, all related activities for the structural steel have to be completed and approved by QC. All scaffolds on the pipe racks have to be completed, inspected, and tagged.
2- Upon arrival at the site, the numbers and markings of all spools and materials shall be checked and verified against the erection drawings. The spools and full-length pipes will be stored near the pipe racks on timber blocks so that they will not touch the ground directly. If grinding and welding work are to be done before lifting, the pipe shall be put on the stands. The work shall be completed, internally cleaned, and end covers installed on the stands.
3- All the pipes or pipe spools shall also be visually inspected for damages and/or other unacceptable conditions. All pipework damages shall be rectified prior to erection. Flange faces shall be inspected as per Flange Management Procedure prior to erection and any damage on flange faces shall be reported.
4- Erection materials (bolts, nuts, gaskets) shall be requested and stored as per isometrics just prior to erection.
5- All materials (pipes, bolts, nuts, gaskets) shall be in accordance with the applicable specifications and drawing requirements regarding type, grade, and required certification. Inline equipment and temporary bobbins shall be available (where required).
6- Before starting erection at the site, necessary work permits shall be prepared, and approval shall be received from area authorities. A toolbox meeting will be held prior to work commencing. All required PPE shall be used by all the crew. The site will be controlled and boxed with safety bands.
7- The pipe rack will be marked for the exact location of the pipe according to the surveyor's isometric and layout drawings.
8- Where possible, permanent pipe support shoes or trunnions (all pipe supports / guides) shall be fitted, welded, NDT done, and painted before the erection of the associated Pipework.
9- All the members of the pipe crew shall be trained for hub connections, working at height, pipe cutting-grinding works, pipe threading machine operation, piping cleanliness, and flange integrity.
10- Fabric slings shall handle pipes to prevent damage to pipe coatings. Soft-faced hooks in contact with pipes may be used for lifting, provided the hook tip does not damage the pipe internally, or it is determined that lifting with hooks is not safe.
11- Mechanical or hydraulic jacks may be required for internal usage on large piping fit-up works.
ERECTION
1- All pipe spools and straight pipes shall be erected in accordance with the "AFC" issues of the isometric and layout drawings. Isometric drawings shall be marked “AS FABRICATED.”
2- Straight pipes or pipe spools welded on the ground level above the stands (double joint) shall be erected after NDT inspection, PWHT (if required), retro jetting (internal cleaning), internal preservation (VpCI) (if required), and end cap installation.
3- Steel works on the pipe rack (vertical bracing) may be removed for pipe spool installation if necessary. During the installation, chain blocks shall be fixed inside the rack on upper beams, and the pipe spool shall be moved inside using the chain blocks, rollers (if required), and equipment of rigging needed.
4- Pipe rollers (with various capacities) shall be used to position or move the straight pipe spools inside the pipe rack and structures.
5- Straight pipes (6” and above), with minimum ANSI standard pipe thickness, shall not be prepared or welded (on ground level) longer than 36m.
6- Small bore pipes (up to 4”) with a maximum length of 24 m shall be prepared on the ground level.
7- Suitable cranes for lifting or manual devices, such as chain blocks or come-along jacks, shall be used. Cranes shall be positioned in a suitable place around the pipe rack structure. All lifting operations should be done according to lifting procedures.
8- The lifting method for long straight pipes on or inside the pipe rack shall be using one or two cranes according to the cranes' capacity and the pipes' weight. The lifting operation should be studied, and the lifting study should be submitted to the site authority for review and approval.
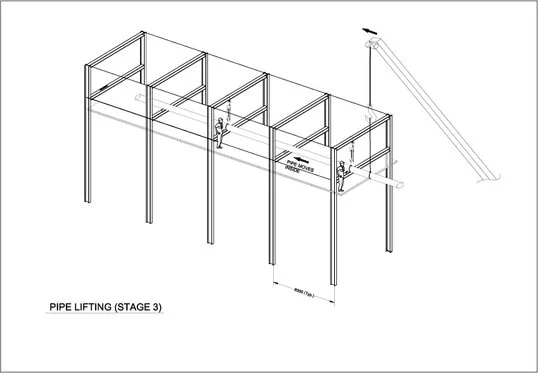
The figures below ‘Pipe Installation in Pipe Rack’ include sketches (typical drawings) about a lifting operation inside a pipe rack using one crane. The sketches explain the base rules of a lifting operation using one crane. Namely;
Before the operation commences, scaffolding must be completed and approved. Then, pipe rollers and chain blocks must be placed and fixed (on upper beams).
Two pipe fitters or riggers shall be ready up on the scaffolding during the lifting operation to help guide the pipe to its project location.
Sufficient capacity chain blocks and rollers shall be hooked to the beams, as shown in the sketches (Attachment 1).
The straight pipe shall be lifted up and moved inside the rack by the crane. After the first section of the pipe is inside the rack on rollers, the first chain block shall be hooked to the pipe and take the load for the first sling.
The pipe shall be moved inside the rack by using a crane. When the pipe is inside the rack (until the last sling) on rollers, the last sling shall be released. Then, the second chain block shall be hooked to draw the pipe to its location.
Please see ‘Pipe Installation in Pipe Rack’ for straight pipe lifting typical drawings in 3 stages.
Pipefitters should only use lifting gear such as chain blocks, pull lifts etc. only for minor alignment of piping, otherwise lifting team is to perform required operations.
The pipe spools shall be lifted, reversing the shoes (looking up) on ground level to allow the pipe to move on rollers. After the lifting operation is completed by the rigging equipment, the pipe shall be reversed, and installation completed.
After each spool is lifted they will be placed dimensionally in its place by using rigging equipment (chain blocks, trifors, rollers etc.). When two spools and/or pipes are placed, fit-up will be done and they will be prepared for inspection prior to welding. Where possible all support guide and stops may be installed and welded prior to erection.
The dimensional checks shall be carried out based on the isometric drawing to ensure that the coordinates and the elevation of the spools are in an accurate position. For that purpose, survey equipment or ropes, level gauges, and straight edges can be used.
After alignment and inspection of the spool, welding shall be commenced. Welding tents shall be installed so that the outside weather shall not affect the weld quality. Rope used for alignment shall be removed following welding and pipe to be supported on pipe supports. The rotating machinery and other equipment discharge flanges shall be fitted with temporary closures (end cap, flange face covers).
For stainless steel pipes, removable foam (purge) dams (to minimize the consumption of backing gas) shall be used.
Due to the line configurations and/or the use of paper dams that cannot be avoided, water-soluble paper can be used for the lines where water flushing and hydro testing shall be carried out.
All temporary welding dams shall be recorded by a QC representative. For that purpose, a ‘request for inspection’ (RFI) form shall be prepared by the pipe welding supervisor, and this form shall be sent to the QC representative.
QC may prepare all data and maintain a Purge Dam Register. The data shall include the type of dam used, the location, and signature/dates of insertion-removal following the inspections.
All valves shall be installed in the open position, as shown on the piping drawings.
All the valves shall be checked, cleaned, and stroked prior to installation.
Valves shall be positively protected so as to prevent the ingress of dust, dirt, and moisture into the valve at all times prior to or after installation into the line.
Heavy valves and fittings shall be adequately supported before the Pipework is erected or subjected to pressure test.
The erection will follow the latest layout and isometric drawings, and all in-line instruments, valves, orifice plates, supports, etc., shall be installed during the erection (where permissible). This will ensure the total system dimensionally fits as per the drawings.
During grinding and welding works on C.S. lines, a fire blanket shall be used to protect SS lines from any contaminants. Care shall be taken to prevent any contact with carbon steel material or stainless steel materials. Foam bungs shall be used and inserted into the spools to stop and ingress of dirt or grinding matter until it is ready to be tack welded. Foam bungs shall be removed before tack welding/fit-up.
HSE
All necessary work permits for the activity shall be received before starting the work.
Any works carried out in the commissioning-owned area are to be carried out under commissioning CoW.
Prior to any activities commencement work site is to be assessed for SIMOPS (if any) and relevant parties is to agree on works interfaces and key points. Only upon reached agreement both works may proceed.
Prior to any how work activities (including use of grinders etc.) hot work check sheet shall be completed.
Pipefitters must be fully informed of the correct erection sequence, by the supervisor, prior to each stage of work commencing. Supervisor shall refer to Task Risk Assessment which is prepared specifically for this work.
Prior to commencing work, the Supervisor and foreman will ensure that all workers have all necessary, appropriate PPE (minimum hard hat, safety glasses, safety footwear, safety clothing, and gloves) and that they properly wear PPE to perform the work safely. Where it is not practicable to provide a standard working platform, all workers working at height shall wear full-body safety harnesses with dual lanyards, which shall be attached to an adequate load-bearing point or lifeline or inertia reel.
A confined space work permit is required for large pipe internal cleaning and fit-up works. The pipe internals shall be cleaned using an air compressor.
Additional PPE will be required, such as a respirator and earplugs, during air-blown cleaning. The TRA must be ready and approved by the Company prior to work commencing.
Welders shall wear additionally:
· Face and eye protection with the correct grade of filter integrated into the Safety helmet.
· Welder gauntlets.
· Long-sleeved flame retardant overalls.
Prescribed safety precautions, manufacturer’s instruction guides, and fire prevention guidelines shall be followed.
A Daily Crane inspection shall be conducted and reported for any fault before starting the work. Only certified and inspected cranes and lifting equipment, color-coded properly, shall be used. Necessary safety signs to warn workers and passers-by shall be posted.
All dies shall be checked and set correctly, with no worn edges or missing points.
The tools shall be cleaned and regularly wiped out.
There shall be a sufficient supply of clean coolant (recommended and company-approved), and all filters shall be clean and functioning.
Untrained persons shall not operate the threading machines or equipment.
Heavy-duty work gloves and safety goggles shall be used.
During the operation, hands, fingers, feet, and any loose items (ties, loose clothes, long hairs shall be tied up) shall be kept away from the threatening machine.
Damaged threading equipment shall not be used.
Threading equipment shall be used on proper footing and balanced at all times.
Threading machine shall be used on solid ground preferably concrete.






This blog is intended as a guide to determining the minimum safe spacing of plants and equipment in Oil Refineries, Petrochemical Complexes, and similar installations.
The spacing recommendations will apply in the absence of Clients' standards or supplement such standards where necessary. They are based on current industry practice.
The spacing recommendations aim to ensure that available plot areas are used economically without affecting personnel safety or plant vulnerability.